Posts Tagged ‘privacy’
Facebook dialogue
Tags: Facebook, getting social, presentation of the self, privacy
Posted in social web | Comments (0)
Quantified Self & Privacy: some brief thoughts before the breakout session
Today at 3 (in Heidelberg) I’m running a breakout session on QS & Privacy: How can we ensure privacy as we share our data stories? What rights and responsibilities do we have? Where is the public-prviate boundary?
Here are a few provocative thoughts from conversations so far today.
Body Blogger Kiel Gilleade talked about heartrate this morning:
My boss called me to ask whether I was working on a deadline because my heart rate was in the green zone rather than in the red zone like the last paper-writing deadline.
He observes: situational & contextual info is crucial for interpretation.
Tom Hume tweeted:
You don’t control your identity. It’s manufactured by those around you. #qs2011
Joshua Kauffman tweeted:
There is no such thing as personal health data. All matters of health are socially shared and derived. #qs2011
Tags: privacy, QS11, QS2011, QuantifiedSelf, QuantifiedSelfEurope, self-surveillance
Posted in random thoughts, social web | Comments (1)
Quantified Self Europe, two talks proposed
Thanksgiving weekend doesn’t really register in Europe. But this year it will for me: I’m going to Amsterdam for Quantified Self Europe, since I’m lucky enough to have a scholarship covering conference fees.
Today I proposed two talks:
- Weight and exercise tracking (which I’ve been doing in various forms for 19 months, currently using a Phillips DirectLife exercise monitor, and a normal scale, collected with the hacker’s diet). Mainly, these are less integrated than they could be, and I’d like to advocate interoperability, APIs, and uniform formats — while hopefully getting some ideas from the audience about quick hacks to improve my current system.
- Lifetracking, privacy & the surveillance society. This brings together two themes: First, how individuals’ lifetracking can be seen as a re-enactment of privacy, with changed ideas of what that means (e.g. panopticon, sousveillance, etc.). Second, the increased awareness about the wealth of personal data held by corporations (e.g. German politician Malt Spitz sued to get 6 months of his telcom data). The boundary between public life and private life is continually shifting as communication technology and social norms evolve; this talk investigates how lifetracking and the quantified self movement push the privacy/publicity boundaries in multiple ways. QS increases the public audience for data-driven stories of private lives while also highlighting the need for individuals to control access to and the disposition of their own personal data.
Ironically, self-surveillance was an academic interest of mine before it became a personal one: Back in 2009, Nathan Yau and I wrote a paper for the ASIST Bulletin about self-surveillance (PDF) [less pretty in HTML]. It helped interest me in the Semantic Web, too: putting data in standard formats would make it easier to make data-driven visualizations, so lifetracking and the quantified self movement is a great usecase for the (social) Semantic Web. QS also shows how privacy cuts both ways and could provide an early-adopter audience for the kind of fine-grained privacy tools a colleague is developing.
(A first reply to Nic’s encouragement)
Tags: lifetracking, panopticon, privacy, proposals, Quantified Self, self-surveillance, sousveillance, surveillance
Posted in semantic web, social semantic web | Comments (0)
Surveillance, Personal Edition
Have you ever kept a calendar, tracked what you eat, or saved receipts? Simple data, like how much soda you drink, can tell a story:
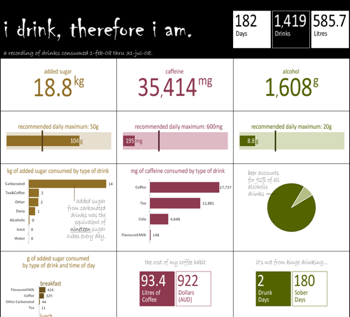
In fact, what you drink can tell several stories. Here’s a more elaborate example, also by Tim Graham:
This is what we call self-surveillance.
What is self-surveillance? Read my article! (Also in PDF). Or Nathan Yau’s blog.
Also added to to the publications page: Nathan Yau & Jodi Schneider “Self-Surveillance,” Bulletin of the American Society for Information Science and Technology Vol. 35, No. 5 June/July 2009, 24-30. [HTML][PDF] . Thanks to Diane Neal (NCCU/U. Western Ontario), who edited the special section on Visual Representation, Search and Retrieval for this issue, and to the Bulletin’s editor Irene Travis and designer Carla Badaracco (who made the 16 figures work for screen and print).
Hat tip to Jenny Levine, whose “How Public is your Privacy” often comes to mind.
Tags: data-collection, privacy, self-surveillance
Posted in information ecosystem, library and information science | Comments (0)