CiTO has escaped the lab and can now be used either directly in the CiteULike interface or with CiteULike machine tags. Go Citation Typing Ontology!
In the CiteULike Interface
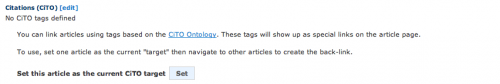
To add a CiTO relationship between articles using the CiteULike interface, both articles must be in your own library. You’ll see a a “Citations (CiTO)” section after your tags. Click on edit and set the current article as the target.
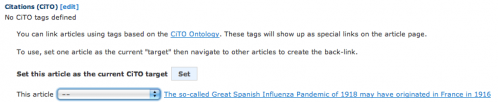
Then navigate around your own library to find a related article. Now you can add a CiTO tag.
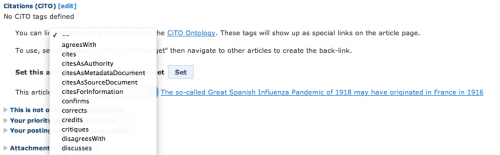
There are a lot of choices. Choose just one. :)
Congratulations, you’ve added a CiTO relationship! Now mousing over the CiTO section will show details on the related article.
Machine Tags
Machine tags take fewer clicks but a little more know-how. They can be added just like any other tag, as long as you know the secret formula: cito--(insert a CiTO Object Property here from this list)--(insert article permalink numbers here) Here are two more concrete examples.
First, we can keep a list of articles citing a paper. For example, tagging an article
cito--cites--1375511
says “this article CiTO:cites article 137511”. Article 137511 can be found at http://www.citeulike.org/article/137511, aka JChemPaint – Using the Collaborative Forces of the Internet to Develop a Free Editor for 2D Chemical Structures. Then we can get the list of (hand-tagged) citations to the article. Look—a community generated reverse citation index!
Second, we can indicate specific relationships between articles, whether or not they cite each other. For example, tagging an article
cito--usesmethodin--423382
says “this item CiTO:usesmethodin item 42338”. Item 42338 is found at http://www.citeulike.org/article/423382, aka The Chemistry Development Kit (CDK): An Open-Source Java Library for Chemo- and Bioinformatics.
Upshot
Automation and improved annotation interfaces will make CiTO more useful. CiTO:cites and CiTO:isCitedBy could used to mark up existing relationships in digital libraries such as ACM Digital Library and CiteSeer, and could enhance collections like Google Books and Mendeley, to make human navigation and automated use easier. To capture more sophisticated relationships, David Shotton has hopes of authors marking up citations before submitting papers; if it’s required, anything is possible. Data curators and article commentators may observe contradictions between papers, or methodology reuses; in these cases CiTO could be layered with an annotation ontology such as AO in order to make the provenance of such assertions clear.
CiTO could put pressure on existing publishers and information providers to improve their data services, perform more data cleanup, or to exposing bibliographies in open formats. Improved tools will be needed, as well as communities that are willing to add data by hand, and algorithms for inferring deep citation relationships.
One remaining challenge is aggregation of CiTO relationships between bibliographic data providers; article identifiers such as DOI are unfortunately not universal, and the bibliographic environment is messy, with many types of items, from books to theses to white papers to articles to reports. CiTO and related ontologies will help explicitly show the bibliographic web and relationships between these items, on the web of (meta)data.
Further Details
CiTO is part of an ecosystem of citations called Semantic Publishing and Referencing Ontologies (SPAR); see also the JISC Open Citation Project which is taking bibliographic data to the Web, and the JISC Open Bibliography Project. For those familiar with Shotton’s earlier writing on CiTO, note that SPAR breaks out some parts of the earlier formulation of this ontology.